- Android Device Manager
- Android Device Manager Remove Lock
- Android Device Manager Android
- Android Device Manager Official Website
- Android Device Manager Locate Phone
- Google Android Device Manager
Several days ago, I got a new Samsung Galaxy S6 from my brother as a birthday present. But I lost it when I went to the cinema. Luckily, I have set Android Device Manager with my Google account on that phone. Can I get back my Samsung phone?
A friend consulted me how to get back her lost new android phone with Android Device Manager. I suppose that many android users probably encountered the same problem. Here, in this article, a detailed introduction of Android Device Manager, together with some good alternatives Android Device Manager, will be described. Now, have a good look at them.
- Android Device Manager is a creative tool that allows users to locate Android devices. There are Android version and website version of it. So, users can find their phone and tablet on both website and another Android. After locating the lost device, it is available to ring the device, change lock screen, send recovery messages, and erase the.
- Feb 20, 2019 Android Device Manager, also named as ADM, is a kind of device managing service designed for Android users by Google Inc, to control their android phone, tablet and other android devices via Google account.
- How to Activate Android Device Manager. What Android Device Manager can do? Android Device Manager makes it easy to locate, ring, or wipe your device from the web. Locate Android devices associated with your Google account. Reset your device's screen lock PIN. Erase all data on the phone.
Download Android Device Manager app for Android. Helps locate stolen or misplaced devices and removes personal data.
Android Device Manager
1 What is Android Device Manager
Android Device Manager, also named as ADM, is a kind of device managing service designed for Android users by Google Inc, to control their android phone, tablet and other android devices via Google account. Its main function is to locate, ring, lock, and erase their android phone or tablet when they lost or misplaced it to make all data on the device safe and secure.
2 How to set up Android Device Manager on your Android device
1. Turn Android Device Manager on.
Before using Android Device Manager, be sure that your Android phone is synced with your Google account and Android Device Manager is on. If not, try to do the following:
Go to 'Google Settings app' > 'Security' > 'Android Device Manager', and tap 'Remotely locate this device', also activate 'Allow remote lock and factory reset'.
2. Turn location access on
3. Prepare to track your android device someday
Google Android Device Manager also runs on tablets. By now, you have enabled Android Device Manager. Next, you can manage your Android devices as you need.
3 How to use Android Device Manager to track/lock phone
We always hope that you will never use this Device Management on Android. However, unfortunately, when you have to use it to track Android phone one day, you can open Android Device Manager App on other phones, or through Android Device Manger website. Then follow the paragraphs below to find out where is your phone.
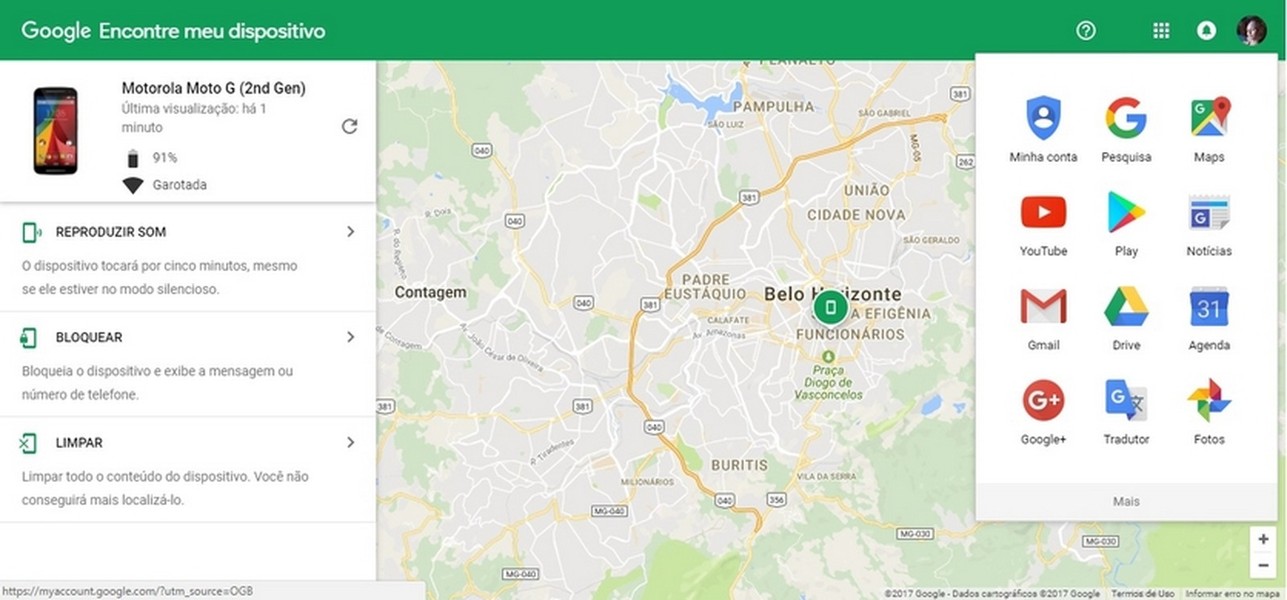
Locate Android phone
1. Log into your Google Account. (Forgot Google password? Recover Google account easily here.)
2. Choose the exact device you are tracking.
3. The Android Manager will show you the approximate location of the device when the lost phone is online.
4. After locating your lost android, you can ring, lock, or wipe all your android phone data remotely to preserve your privacy.
Ring lost phone
Sometimes, you just misplaced your mobile and you cannot find it. So go to this Android Device Management, and click 'Ring', causing your phone to ring for 5 minutes even if it is set on silent or vibrate.
Lock Android phone
When you are sure that you have lost your Android phone and because there are very private things, it is better to lock your mobile just in case. Click 'Lock' option and you need to reset your password twice. From then on, whoever wants to use this phone must use Android Device Manager to unlock it.
Erase data of lost Android
Here is the highest level – Erase Device. If you are so worried about your privacy and want to remove all of your photos, contacts, videos, messages, app, etc on your phone or tablet, you can wipe your Android device remotely. Just click 'Erase Device', like factory reset, and it will clear your phone. But the things on your SD card maybe not removed.
4 How to unlock Android Device Manager
If you have found back your lost phone, you can unlock it by inputting the PIN password or pattern. However, if you are forgetful, or your phone was back after a long time, and you forget the password or pattern, you still can unlock Android Device Manager to use your phone freely.
For removing Android Device Manager lock, you need to meet the following rules:
1. ADM will have to be enabled on your phone before it is lost, stolen, etc.
2. The GPS option must be turned on in order to track your phone with the help of ADM.
3. The phone you are using with ADM has to be connected to the Internet or Wi-Fi.
4. Your phone must be running Android 4.4 and above.
Now, let's show the process to unlock ADM.
Step 1. Go to google.com/android/devicemanager on your computer or any other mobile phone. Sign in to your Google account enabled ADM.
Step 2. In the ADM interface, choose the phone you want to unlock and then select 'Lock'.
Step 3. Enter a temporary password and click on 'Lock' again. Then you will see a confirmation with the buttons of Ring, Lock and Erase.
Step 4. Input the temporary password to unlock your phone.
Step 5. Visit your phone's lock screen settings and disable the temporary password.
Now, Android Device Manager lock has been removed from your phone.
5 Alternatives to Android Device Manager
If Android Device Manager location is unavailable, and cannot find your phone location history, you need to find its alternatives, here we recommend you some software to track your Android devices.
Prey is a phone-tracker application which runs silently in the background after you install it. It can track and trigger your lost phone, gather and deliver a picture of who is using it, or remotely lock down and erase everything on your lost device completely. More importantly, it supports almost all major devices, including Android phone or tablet, iOS device, Windows PC and Mac.
Find My iPhone is an app to track your iPhone, iPad or Mac. It was developed by Apple Inc. exclusively for Apple users. When your device goes missing, you need to lock down your device immediately and text a message to the lost device with a contact number by logging in to your iCloud. You can also use Activate Lock to protect your data from the wrong hands. Also, remote erase is available to you to wipe all your data on device when you cannot get it back. It is totally free to use. However, it only supports Apple products.
Where's My Droid is also a phone-track app to help you track and find your lost phone. It can help you locate your lost phone and ring it. It can adjust the ringtone volume up. And it can keep your phone battery consuming less after losing it. It has a free version with limited features. Just have a try.
By now, everything about Android Device Manager is introduced. And we hope that it will bring you convenience to find your lost Android device.
Conclusion
This page mainly talks about Android Device Manager, definition and usage. You can easily set up Android Device Manager to help to track and find your lost phone location. Surely, if you do not want to use it, you can remove the lock easily with the step-by-step guide. Surely, Android Device Manager is not the only tool you can use to locate your lost phone, and you can find the replacement of ADM in the last part to track your lost phone.
Have you grasp the whole usage of ADM? Let me know to leave your comments below.
What do you think of this post?
Excellent
Rating: 4.8 / 5 (based on 175 votes)
February 20, 2019 17:30 / Updated by Iris Walker to Android Troubleshooting
- The Best Way to Turn Off Find My iPhone and Activation Lock
Find My iPhone and Activation Lock can protect your iPhone data when you lost your iPhone. However, they stream your battery power. Learn how to turn off find my iPhone from this guide.
- Three Ways of Backing up Android Contacts to PC
Before you lose your Samsung Galaxy S4 and all your contacts? Learn how to back up Android contacts to PC from this article.
- How to Manage HTC Phone with HTC Sync Manager on Computer
HTC users will not miss this article to use HTC Manager to sync HTC data on computer.
This article explains how to use the Android Device Manager to createand configure Android Virtual Devices (AVDs) that emulate physical Androiddevices. You can use these virtual devices to run and test your appwithout having to rely on a physical device.
After you have verified that hardware acceleration is enabled (asdescribed inHardware Acceleration for Emulator Performance),the next step is to use the Android Device Manager (also referred toas the Xamarin Android Device Manager) to create virtual devices thatyou can use to test and debug your app.
Android Device Manager on Windows
This article explains how to use the Android Device Manager to create,duplicate, customize, and launch Android virtual devices.
You use the Android Device Manager to create and configure AndroidVirtual Devices (AVDs) that run in theAndroid Emulator.Each AVD is an emulator configuration that simulates a physical Androiddevice. This makes it possible to run and test your app in a variety ofconfigurations that simulate different physical Android devices.
Requirements
To use the Android Device Manager, you will need the following items:
Visual Studio 2019 Community, Professional, or Enterprise.
OR Visual Studio 2017 version 15.8 or later is required. Visual StudioCommunity, Professional, and Enterprise editions are supported.
Visual Studio Tools for Xamarin version 4.9 or later.
The Android SDK must be installed (seeSetting up the Android SDK for Xamarin.Android).Be sure to install the Android SDK at its default location if itis not already installed: C:Program Files (x86)Androidandroid-sdk.
The following packages must be installed (via theAndroid SDK Manager):
- Android SDK Tools version 26.1.1 or later
- Android SDK Platform-Tools 27.0.1 or later
- Android SDK Build-Tools 27.0.3 or later
- Android Emulator 27.2.7 or later.
These packages should be displayed with Installed status as seen inthe following screenshot:
Launching the Device Manager
Launch the Android Device Manager from the Tools menu byclicking Tools > Android > Android Device Manager:
If the following error dialog is presented on launch, see theTroubleshooting section for workaroundinstructions:
Main Screen
When you first launch the Android Device Manager, it presents a screenthat displays all currently-configured virtual devices. For eachvirtual device, the Name, OS (Android Version), Processor,Memory size, and screen Resolution are displayed:
When you select a device in the list, the Start button appears onthe right. You can click the Start button to launch the emulatorwith this virtual device:
After the emulator starts with the selected virtual device, theStart button changes to a Stop button that you can use to haltthe emulator:
New Device
To create a new device, click the New button (located in the upperright-hand area of the screen):
Clicking New launches the New Device screen:
To configure a new device in the New Device screen, use thefollowing steps:
Give the device a new name. In the following example, the new deviceis named Pixel_API_27:
Select a physical device to emulate by clicking the Base Devicepull-down menu:
Select a processor type for this virtual device by clicking theProcessor pull-down menu. Selecting x86 will provide thebest performance because it enables the emulator to take advantageof hardware acceleration.The x86_64 option will also make use of hardware acceleration,but it runs slightly slower than x86 (x86_64 is normallyused for testing 64-bit apps):
Select the Android version (API level) by clicking the OSpull-down menu. For example, select Oreo 8.1 - API 27 to createa virtual device for API level 27:
If you select an Android API level that has not yet been installed, theDevice Manager will display A new device will be downloadedmessage at the bottom of the screen – it will download andinstall the necessary files as it creates the new virtual device:
If you want to include Google Play Services APIs in your virtualdevice, enable the Google APIs option. To include the GooglePlay Store app, enable the Google Play Store option:
Note that Google Play Store images are available only for some basedevice types such as Pixel, Pixel 2, Nexus 5, and Nexus 5X.
Edit any properties that you need to modify. To make changes toproperties, seeEditing Android Virtual Device Properties.
Add any additional properties that you need to explicitly set. TheNew Device screen lists only the most commonly-modifiedproperties, but you can click the Add Property pull-down menu(at the bottom) to add additional properties:
You can also define a custom property by selecting Custom... atthe top of the property list.
Click the Create button (lower right-hand corner) to create thenew device:
You might get a License Acceptance screen. Click Accept ifyou agree to the license terms:
The Android Device Manager adds the new device to the list ofinstalled virtual devices while displaying a Creating progressindicator during device creation:
When the creation process is complete, the new device is shown inthe list of installed virtual devices with a Start button,ready to launch:
Edit Device
To edit an existing virtual device, select the device and click theEdit button (located in the upper right-hand corner of the screen):
Clicking Edit launches the Device Editor for the selected virtual device:
The Device Editor screen lists the properties of the virtual deviceunder the Property column, with the corresponding values of each property inthe Value column. When you select a property, a detailed descriptionof that property is displayed on the right.
To change a property, edit its value in the Value column.For example, in the following screenshot the hw.lcd.density propertyis being changed from 480 to 240:
After you have made the necessary configuration changes, click the Save button.For more information about changing virtual device properties, seeEditing Android Virtual Device Properties.
Additional Options
Additional options for working with devices are available from theAdditional Options (…) pull-down menu in the upperright-hand corner:
The additional options menu contains the following items:
Duplicate and Edit – Duplicates the currently-selecteddevice and opens it in the New Device screen with a differentunique name. For example, selecting Pixel_API_27 and clickingDuplicate and Edit appends a counter to the name:
Reveal in Explorer – Opens a Windows Explorer window in thefolder that holds the files for the virtual device. For example,selecting Pixel_API_27 and clicking Reveal in Explorer opensa window like the following example:
Factory Reset – Resets the selected device to its defaultsettings, erasing any user changes made to the internal state of thedevice while it was running (this also erases the currentQuick Bootsnapshot, if any). This change does not alter modifications that youmake to the virtual device during creation and editing. A dialog boxwill appear with the reminder that this reset cannot be undone. ClickFactory Reset to confirm the reset:
Delete – Permanently deletes the selected virtual device. Adialog box will appear with the reminder that deleting a devicecannot be undone. Click Delete if you are certain that you wantto delete the device.
Note
If you are using a Mac with an Apple chip, such as the M1, you will need to install the Android Emulator for M1 preview from GitHub.
Android Device Manager on macOS
This article explains how to use the Android Device Manager to create,duplicate, customize, and launch Android virtual devices.
You use the Android Device Manager to create and configure AndroidVirtual Devices (AVDs) that run in theAndroid Emulator.Each AVD is an emulator configuration that simulates a physical Androiddevice. This makes it possible to run and test your app in a variety ofconfigurations that simulate different physical Android devices.
Requirements
To use the Android Device Manager, you will need the following items:
Visual Studio for Mac 7.6 or later.
The Android SDK must be installed (seeSetting up the Android SDK for Xamarin.Android).
The following packages must be installed (via theAndroid SDK Manager):
- SDK tools version 26.1.1 or later
- Android SDK Platform-Tools 28.0.1 or later
- Android SDK Build-Tools 26.0.3 or later
These packages should be displayed with Installed status as seen inthe following screenshot:
Launching the Device Manager
Launch the Android Device Manager by clicking Tools > Device Manager:
If the following error dialog is presented on launch, see theTroubleshooting section for workaroundinstructions:
Main Screen
When you first launch the Android Device Manager, it presents a screenthat displays all currently-configured virtual devices. For eachvirtual device, the Name, OS (Android Version), Processor,Memory size, and screen Resolution are displayed:
When you select a device in the list, the Play button appears onthe right. You can click the Play button to launch the emulatorwith this virtual device:
After the emulator starts with the selected virtual device, thePlay button changes to a Stop button that you can use to haltthe emulator:
When you stop the emulator, you may get a prompt asking if you want to savethe current state for the next quick boot:
Saving the current state will make the emulator boot faster when this virtualdevice is launched again. For more information about Quick Boot, seeQuick Boot.
New Device
To create a new device, click the New Device button (located in the upperleft-hand area of the screen):
Clicking New Device launches the New Device screen:
Use the following steps to configure a new device in the New Devicescreen:
Give the device a new name. In the following example, the new deviceis named Pixel_API_27:
Select a physical device to emulate by clicking the Base Devicepull-down menu:
Select a processor type for this virtual device by clicking theProcessor pull-down menu. Selecting x86 will provide thebest performance because it enables the emulator to take advantageof hardware acceleration.The x86_64 option will also make use of hardware acceleration,but it runs slightly slower than x86 (x86_64 is normallyused for testing 64-bit apps):
Select the Android version (API level) by clicking the OSpull-down menu. For example, select Oreo 8.1 - API 27 to createa virtual device for API level 27:
If you select an Android API level that has not yet been installed,the Device Manager will display A new device will be downloadedmessage at the bottom of the screen – it will download andinstall the necessary files as it creates the new virtual device:
If you want to include Google Play Services APIs in your virtualdevice, enable the Google APIs option. To include the GooglePlay Store app, enable the Google Play Store option:
Note that Google Play Store images are available only for some basedevice types such as Pixel, Pixel 2, Nexus 5, and Nexus 5X.
Edit any properties that you need to modify. To make changes toproperties, seeEditing Android Virtual Device Properties.
Add any additional properties that you need to explicitly set. TheNew Device screen lists only the most commonly-modifiedproperties, but you can click the Add Property pull-down menu(at the bottom) to add additional properties:
You can also define a custom property by clicking Custom...at the top of this property list.
Click the Create button (lower right-hand corner) to create thenew device:
The Android Device Manager adds the new device to the list ofinstalled virtual devices while displaying a Creating progressindicator during device creation:
When the creation process is complete, the new device is shown inthe list of installed virtual devices with a Start button,ready to launch:
Edit Device
To edit an existing virtual device, select the Additional Optionspull-down menu (gear icon) and select Edit:
Clicking Edit launches the Device Editor for the selected virtual device:
The Device Editor screen lists the properties of the virtual deviceunder the Property column, with the corresponding values of each property inthe Value column. When you select a property, a detailed descriptionof that property is displayed on the right.
Android Device Manager
To change a property, edit its value in the Value column.For example, in the following screenshot the hw.lcd.density propertyis being changed from 480 to 240:
After you have made the necessary configuration changes, click the Save button.For more information about changing virtual device properties, seeEditing Android Virtual Device Properties.
Additional Options
Additional options for working with a device are available from thepull-down menu located to the left of the Play button:
The additional options menu contains the following items:

Edit – Opens the currently-selected device in the deviceeditor as described earlier.
Duplicate and Edit – Duplicates the currently-selecteddevice and opens it in the New Device screen with a differentunique name. For example, selecting Pixel 2 API 28 and clickingDuplicate and Edit appends a counter to the name:
Reveal in Finder – Opens a macOS Finder window in thefolder that holds the files for the virtual device. For example,selecting Pixel 2 API 28 and clicking Reveal in Finder opensa window like the following example:
Factory Reset – Resets the selected device to its defaultsettings, erasing any user changes made to the internal state of thedevice while it was running (this also erases the currentQuick Bootsnapshot, if any). This change does not alter modifications that youmake to the virtual device during creation and editing. A dialog boxwill appear with the reminder that this reset cannot be undone. ClickFactory Reset to confirm the reset.
Delete – Permanently deletes the selected virtual device. Adialog box will appear with the reminder that deleting a devicecannot be undone. Click Delete if you are certain that you wantto delete the device.
Troubleshooting
The following sections explain how to diagnose and work around problemsthat may occur when using the Android Device Manager to configurevirtual devices.
Android SDK in Non-Standard Location
Typically, the Android SDK is installed at the following location:
C:Program Files (x86)Androidandroid-sdk
If the SDK is not installed at this location, you may get this error when you launchthe Android Device Manager:
To work around this problem, use the following steps:
From the Windows desktop, navigate toC:UsersusernameAppDataRoamingXamarinDeviceManager:
Double-click to open one of the log files and locate the Configfile path. For example:
Navigate to this location and double-click user.config to open it.
In user.config, locate the
<UserSettings>element and add anAndroidSdkPath attribute to it. Set this attribute to the pathwhere the Android SDK is installed on your computer and save thefile. For example,<UserSettings>would look like the following ifthe Android SDK was installed at C:ProgramsAndroidSDK:
After making this change to user.config, you should be able tolaunch the Android Device Manager.
Wrong Version of Android SDK Tools
If Android SDK tools 26.1.1 or later is not installed, you may see thiserror dialog on launch:
If you see this error dialog, click Open SDK Manager to open theAndroid SDK Manager. In the Android SDK Manager, click the Toolstab and install the following packages:
Android Device Manager Remove Lock
- Android SDK Tools 26.1.1 or later
- Android SDK Platform-Tools 27.0.1 or later
- Android SDK Build-Tools 27.0.3 or later
Snapshot disables WiFi on Android Oreo
If you have an AVD configured for Android Oreo with simulated Wi-Fi access,restarting the AVD after a snapshot may cause Wi-Fi access to become disabled.
To work around this problem,
Select the AVD in the Android Device Manager.
From the additional options menu, click Reveal in Explorer.
Navigate to snapshots > default_boot.
Delete the snapshot.pb file:
Restart the AVD.
After these changes are made, the AVD will restart in a state thatallows Wi-Fi to work again.
Wrong Version of Android SDK Tools
If Android SDK tools 26.1.1 or later is not installed, you may see thiserror dialog on launch:
If you see this error dialog, click OK to open the Android SDKManager. In the Android SDK Manager, click the Tools tab andinstall the following packages:
- Android SDK Tools 26.1.1 or later
- Android SDK Platform-Tools 28.0.1 or later
- Android SDK Build-Tools 26.0.3 or later
Snapshot disables WiFi on Android Oreo
If you have an AVD configured for Android Oreo with simulated Wi-Fi access,restarting the AVD after a snapshot may cause Wi-Fi access to become disabled.
To work around this problem,
Select the AVD in the Android Device Manager.
From the additional options menu, click Reveal in Finder.
Navigate to snapshots > default_boot.
Delete the snapshot.pb file:
Restart the AVD.
After these changes are made, the AVD will restart in a state thatallows Wi-Fi to work again.
Generating a Bug Report
Android Device Manager Android

Android Device Manager Official Website
If you find a problem with the Android Device Manager thatcannot be resolved using the above troubleshooting tips, please file abug report by right-clicking the title bar and selecting Generate BugReport:
Android Device Manager Locate Phone
If you find a problem with the Android Device Manager thatcannot be resolved using the above troubleshooting tips, please file abug report by clicking Help > Report a Problem:
Summary
This guide introduced the Android Device Manager available in VisualStudio Tools for Xamarin and Visual Studio for Mac. It explainedessential features such as starting and stopping the Android emulator,selecting an Android virtual device (AVD) to run, creating new virtualdevices, and how to edit a virtual device. It explained how toedit profile hardware properties for further customization, and itprovided troubleshooting tips for common problems.
Related Links
Google Android Device Manager
Related Video
Find more Xamarin videos on Channel 9 and YouTube.